Classification of hypertension drugs pdf
n engl j med 351;14 www.nejm.org september 30, 2004 The new england journal of medicine 1425 review article drug therapy Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
3 work and hypertension drugs. The choice of the appropriate anti-hypertensive drugs depends on a lot of factors such as severity of the disease, impact of the disease on daily activities,
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a pathophysiological condition defined as an increase in mean pulmonary arterial pressure ≥25 mmHg at rest assessed by right heart catheterization.
Hypertension Main Page Generic Name Listing Brand Name Listing LINKS BELOW ARE BEING CONSTRUCTED. WE HOPE TO HAVE IT COMPLETED SOON. IN THE MEANTIME, USE THE MENU ABOVE TO LOOK UP BRAND NAMES, GENERICS, AND
Antihypertensive drugs are used in the treatment of high blood pressure. Hypertension is not an insignificant diagnosis. It is linked to a substantially increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
Hypertension [1-16, 46-64], or high blood pressure, is a very common and serious condition that can lead to or complicate many health problems. The risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality is directly
Although different classification schemes have been proposed, the first scheme (Vaughan-Williams) is still the one that most physicians use when speaking of antiarrhythmic drugs. The following table shows the Vaughan-Williams classification and the basic mechanism of action associated with each class.
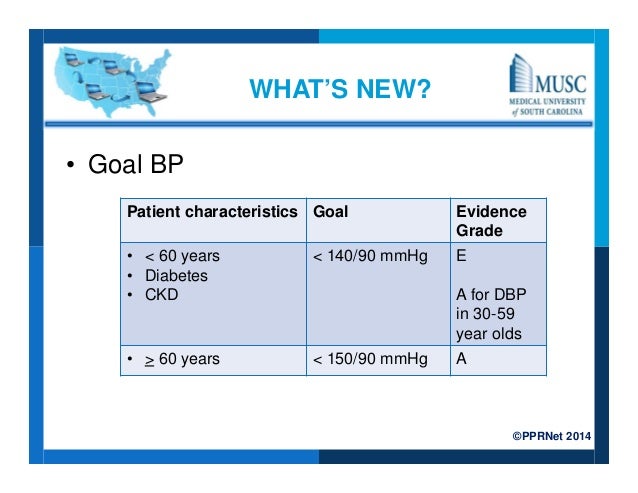
The lower BP levels to start treating hypertension with drugs in cardiovascular (CV) risk patients. The lower BP goals for treated hypertensive patients. Let’s examine these differences point by point: 1. A new classification for hypertension. The biggest change of the 2017 ACC/AHA guidelines is the revision of the BP categories in hypertension. Figure 1 illustrated these differences. In
In a meta-analysis of 190 monotherapy trials in patients with essential hypertension, discontinuations due to adverse events were commoner with calcium channel blocking drugs (6.7%) than with diuretics or angiotensin receptor blockers (3.1% for each).
1. Persistently high arterial blood pressure, defined as systolic blood pressure above 140 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure above 90 mm Hg. 2. Blood pressure range SBP/DBP…
related PH, porto-pulmonary hypertension, HIV-related PH, collagen vascular diseases, congenital systemic-to- pulmonary shunts, and persistent PH of the newborn.
Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC). Numerous antihypertensive drugs, from a variety of pharmacologic classes and with …
British Hypertension Society: classification of blood pressure levels It is impossible to provide a precise definition of hypertension since blood pressure is a continuous variable within the population, having a skewed normal distribution.
medications suggested in this document. Acknowledgements: Dr. S. Britton . 2 These materials were developed by the clinical subcommittee of the Chronic Disease Network and Access Program of the Prince Albert Grand Council and its partners and funded by the Aboriginal Health Transition Fund. Table of Contents Risk Factors for Hypertension 3 Benefits of Treating Hypertension 3 Blood Pressure
Rationale for Pharmacologic Treatment of Hypertension. Patients with primary hypertension are generally treated with drugs that 1) reduce blood volume (which reduces central venous pressure and cardiac output), 2) reduce systemic vascular resistance, or 3) reduce …
Classification of Pulmonary Hypertension Dana McGlothlin, MD INTRODUCTION Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a condition of many causes in which there is an elevation in
Classification of Pulmonary Hypertension
https://youtube.com/watch?v=1SsYduKxE0Q
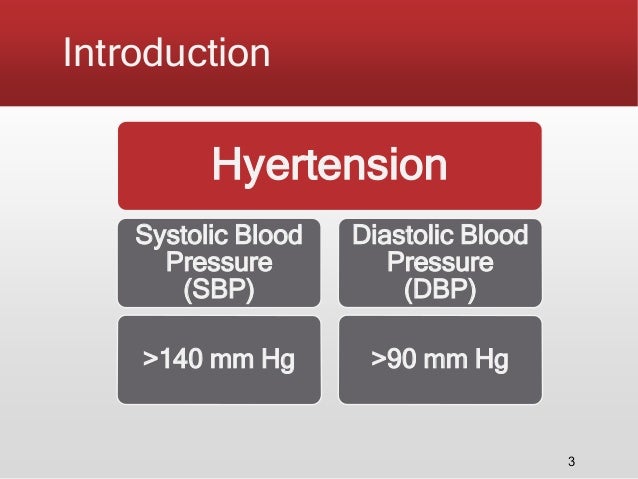
Hypertension Classification of HTN – [PDF Document]
Drugs with β-blocking activity slow the heart rate and decrease the force of contraction of muscles, thus these drugs are useful in treating hypertension and cardiac arrythmias, in addition to angina.
The classification scheme used to classify pulmonary hypertension is in part based on clinical pre- sentation, in part based on physiology, and in part based on treatment implications. Treatment can vary greatly depending on the type of pulmonary hypertension, thus proper diag-
Drug treatment is recommended in severe hypertension in pregnancy (BP >160/110 mmHg), and may be considered in case of persistent BP ≥ 150/95 mmHg, and in those with BP ≥ 140/90 mmHg in the presence of gestational hypertension, asymptomatic organ damage or symptoms.
Gestational hypertension is defined as the de novo development of high blood pressure after 20 weeks gesta- tion, without any of the abnormalities that define pre-
The new guidelines for the classification of hypertension and the list of cardiovascular risk factors provided by JNC-7 are more helpful to oral and maxillofacial surgeons …
5th World Symposium Classification, Nice, France 2013 Group Subcategory I Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (Includes all causes that lead to structural narrowing of the pulmonary vessels) • 1.1 Idiopathic PAH • 1.2 Heritable PAH • 1.3 Drug and toxin induced PAH • 1.4 PAH associated with: Connective tissue diseases, HIV, Portal hypertension, Congenital heart disease, Schistosomiasis
Definition of hypertension in pregnancy Page 3 2. Recording blood pressure in pregnancy Page 4 3. Classification of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy Page 4 4. Investigation of new onset hypertension in pregnancy Page 7 5. Management of preeclampsia and gestational hypertension Page 8 6. Fetal Surveillance Page 13 7. Resolution of preeclampsia Page 15 8. Management of chronic hypertension …
Less than 10% of patients with high blood pressure have secondary Htn.1 angiotensin-aldosterone system (secondary Htn is caused by an underlying medical condition or medication (see table 1).
older than 60) have high blood pressure. The clinical management of hypertension is one of the most common interventions in primary care, accounting for approximately £1billion in drug costs alone in …
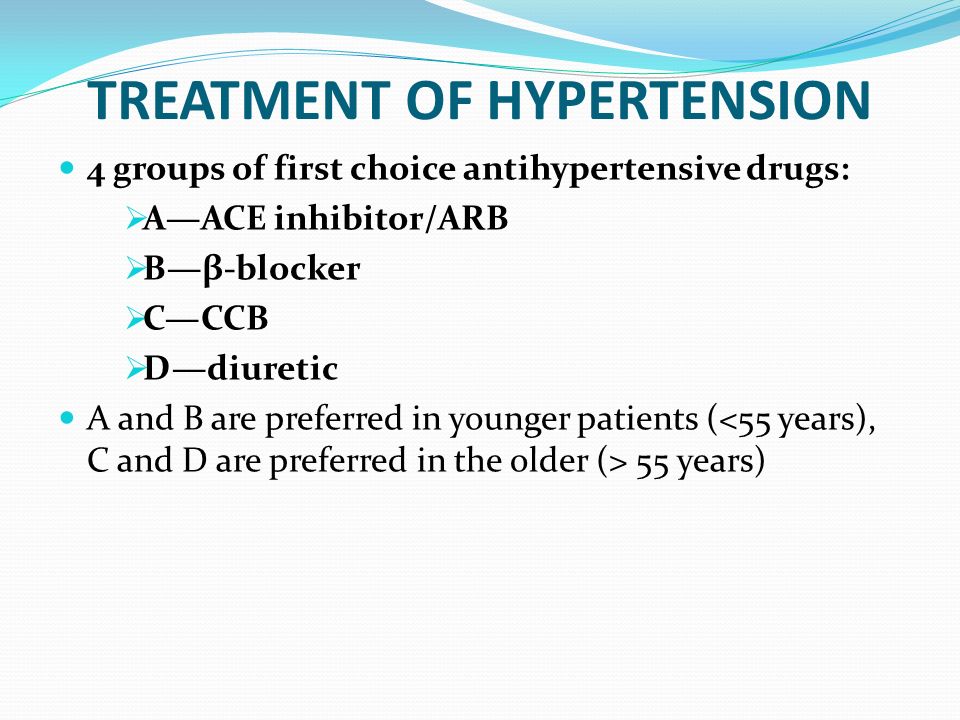
Calcium Channel Blockers – Classification Calcium Channel Blockers – Mechanism of action Calcium Channel Blockers Calcium Channel Blockers – current status Calcium Channel Blockers Vasodilators – Hydralazine Vasodilators – Minoxidil Sodium Nitroprusside Centrally acting Drugs Treatment of hypertension Treatment of Hypertension: 7 classification Treatment of Hypertension – Treatment …
of developing hypertension. * Provide lifestyle modification. If systolic and diastolic categories are different, follow recommendations for the shorter time follow-up (e.g. 160/86
Medicines Management Programme Preferred Drugs Calcium Channel Blockers (dihydropyridine derivatives) for the treatment of hypertension and stable angina
National High Blood Pressure Education Program Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on JNC 7 Express U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National …
Antihypertensive drug classification The antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure). Evidence suggests that reduction of the blood pressure by 5 mmHg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34%, of ischaemic heart disease by 21%, and reduce the likelihood of dementia , heart failure , and mortality from cardiovascular disease . [2]
Rationale for Pharmacologic Treatment of Hypertension. Patients with primary hypertension are generally treated with drugs that 1) reduce blood volume (which reduces central venous pressure and cardiac output), 2) reduce systemic vascular resistance, or 3) reduce cardiac output by depressing heart rate and stroke volume.
Hypertension is already a highly prevalent cardiovascular risk factor worldwide because of increasing longevity and prevalence of contributing factors such as obesity. Whereas the treatment of hypertension has been shown to prevent cardiovascular diseases and to extend and enhance life, hypertension remains inadequately managed everywhere.
Blood Pressure Goal for Patients With Hypertension 5. Drug Therapy 5. Lifestyle Therapy 9. Follow-up and Patient Adherence to Treatment 9 . Hypertension in Patients With Comorbidities 9. Blood Pressure Components, Risk, and Comorbidities of Hypertension 10. Coexistence of Hypertension and Related Chronic Conditions 11. Prevalence and Lifetime Risk of Hypertension 12. Special Patient Groups 12
Hypertension -Complications and Social Impact Dr. Ho Hung Kwong, Duncan 何鴻光 MBBS(HK), MRCP(UK), FHKAM(Med), FHKCP, FRCP(Edin) FAHA, FSCAI Specialist in Cardiology Definition and classification of hypertension: JNC VII Hypertension is defined as blood pressure ≥140/90 mmHg Stage 2 hypertension ≥160 or ≥100 Stage 1 hypertension 140-159 or 90-99 Prehypertension 120 …
established hypertension and identification of individuals with high blood pressure who are at increased risk of complications; and at promoting integration of prevention of hypertension into primary health care settings, including lifestyle measures for
Classification of Blood Pressure Levels by Ambulatory Blood Pressure in Hypertension Andreas Bur, Harald Herkner, Marianne Vlcek, Christian Woisetschläger,
The Ibaraki Prefectural Health Study, including 87 890 individuals (29 917 men and 57 973 women) aged from 40 to 79 years, documented that a mild hypertensive retinopathy (grades 1 and 2 according to Keith–Wagener–Barker classification) was an independent predictor of cardiovascular mortality among Japanese men and women, with or without hypertension .
Blood Pressure Classification National-Academies.org
Updated Clinical Classification of Pulmonary Hypertension Gerald Simonneau, MD,* Michael A. Gatzoulis, Pulmonary Hypertension A number of drugs and toxins have been identified as risk fac-torsforthedevelopmentofPAH and were included in the previous classification (3). Risk factors were categorized according to the strength of evidence, as defi-nite, likely, possible, or unlikely (Table
diseases, drugs and toxins, HIV, portal hypertension, hemoglobinopathies, and myeloproliferative disorders. The diagnosis of PAH requires confirmation with a complete right heart catheterization.
Stage 2 Hypertension ≥ 160 or ≥100 Stage 1 Hypertension 140 -159 or 90 -99 Prehypertension 120 -139 or 80 -89 Normal <120 and <80 DBP mmHg SBP
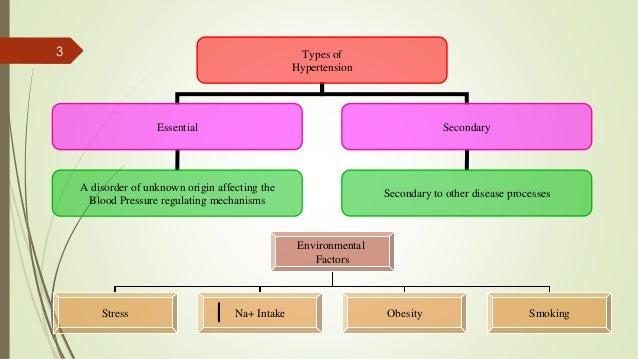
Hypertension Etiology & Classification – Primary (essential) hypertension is the term applied to the 95% of cases in which no cause for hypertension can be identified.
HypertensionComplications and Social Impact
CDNAP 2009 Management of Hypertension
Clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension
Hypertension Guidelines European Heart Journal Oxford
Updated Clinical Classification of Pulmonary Hypertension
Hypertension Etiology & Classification health

CLASSIFICATION AND DIAGNOSIS OF HYPERTENSION
Updated classification of hypertensive retinopathy which
Classification of Blood Pressure Levels by Ambulatory

(PDF) Definition and Classification of Pulmonary Hypertension
Hypertension Classification Pathophysiology And
Classification of Blood Pressure Levels by Ambulatory
Clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension
Antihypertensive drugs are used in the treatment of high blood pressure. Hypertension is not an insignificant diagnosis. It is linked to a substantially increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
older than 60) have high blood pressure. The clinical management of hypertension is one of the most common interventions in primary care, accounting for approximately £1billion in drug costs alone in …
Definition of hypertension in pregnancy Page 3 2. Recording blood pressure in pregnancy Page 4 3. Classification of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy Page 4 4. Investigation of new onset hypertension in pregnancy Page 7 5. Management of preeclampsia and gestational hypertension Page 8 6. Fetal Surveillance Page 13 7. Resolution of preeclampsia Page 15 8. Management of chronic hypertension …
Calcium Channel Blockers – Classification Calcium Channel Blockers – Mechanism of action Calcium Channel Blockers Calcium Channel Blockers – current status Calcium Channel Blockers Vasodilators – Hydralazine Vasodilators – Minoxidil Sodium Nitroprusside Centrally acting Drugs Treatment of hypertension Treatment of Hypertension: 7 classification Treatment of Hypertension – Treatment …
British Hypertension Society: classification of blood pressure levels It is impossible to provide a precise definition of hypertension since blood pressure is a continuous variable within the population, having a skewed normal distribution.
The new guidelines for the classification of hypertension and the list of cardiovascular risk factors provided by JNC-7 are more helpful to oral and maxillofacial surgeons …
of developing hypertension. * Provide lifestyle modification. If systolic and diastolic categories are different, follow recommendations for the shorter time follow-up (e.g. 160/86
In a meta-analysis of 190 monotherapy trials in patients with essential hypertension, discontinuations due to adverse events were commoner with calcium channel blocking drugs (6.7%) than with diuretics or angiotensin receptor blockers (3.1% for each).
Gestational hypertension is defined as the de novo development of high blood pressure after 20 weeks gesta- tion, without any of the abnormalities that define pre-